Corneal ulcer
Identification and history
- Name: Boby
- Report: Canine, half-breed, neutered male, 8 years old.
Differential diagnosis: suspected corneal ulcer complicated by bacterial infection.
Past medical history: Gastrointestinal symptoms with hematochezia, dysorexia and progressive weight loss.
Ocular Ultrasound Exam
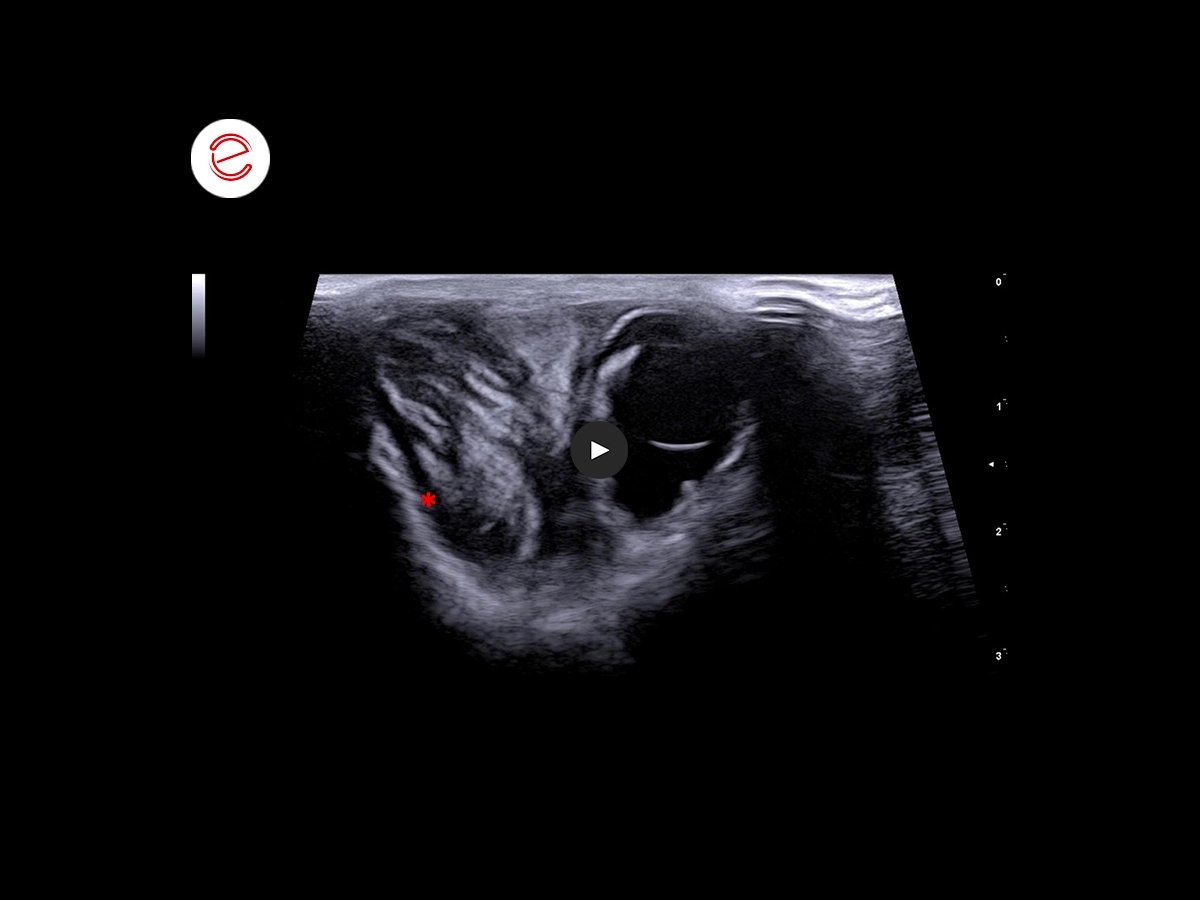
We observed a neoformation on the lateral aspect of the orbital cavity, resulting in compression of the ocular globe. This neoformation has almost well-defined margins, heterogeneous echogenicity with a positive Color Doppler signal.*
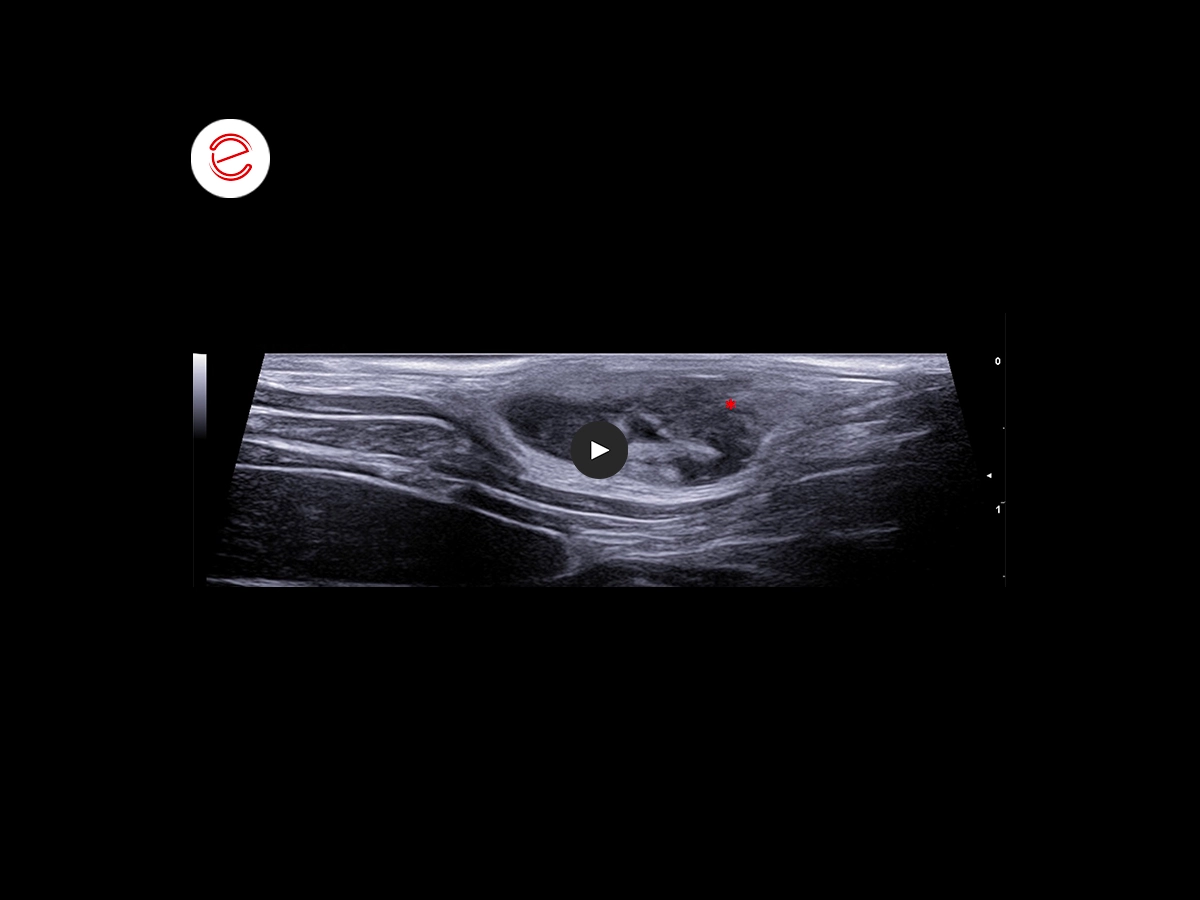
During the clinical examination, at the left flank level, we reported the presence of two subcutaneous lesions, mobile and compact in consistency, which have well-defined margins and heterogeneous echogenicity; positive Color Doppler signal.*
FNA → Cytological exam: "Malignant round cell neoplasm, first hypothesis high-grade lymphoma".
Following the outcome of the cytological examination of the skin and eye lesions, we requested an abdominal ultrasound examination in order to complete the diagnostic procedure for patient staging.
Abdominal Ultrasound
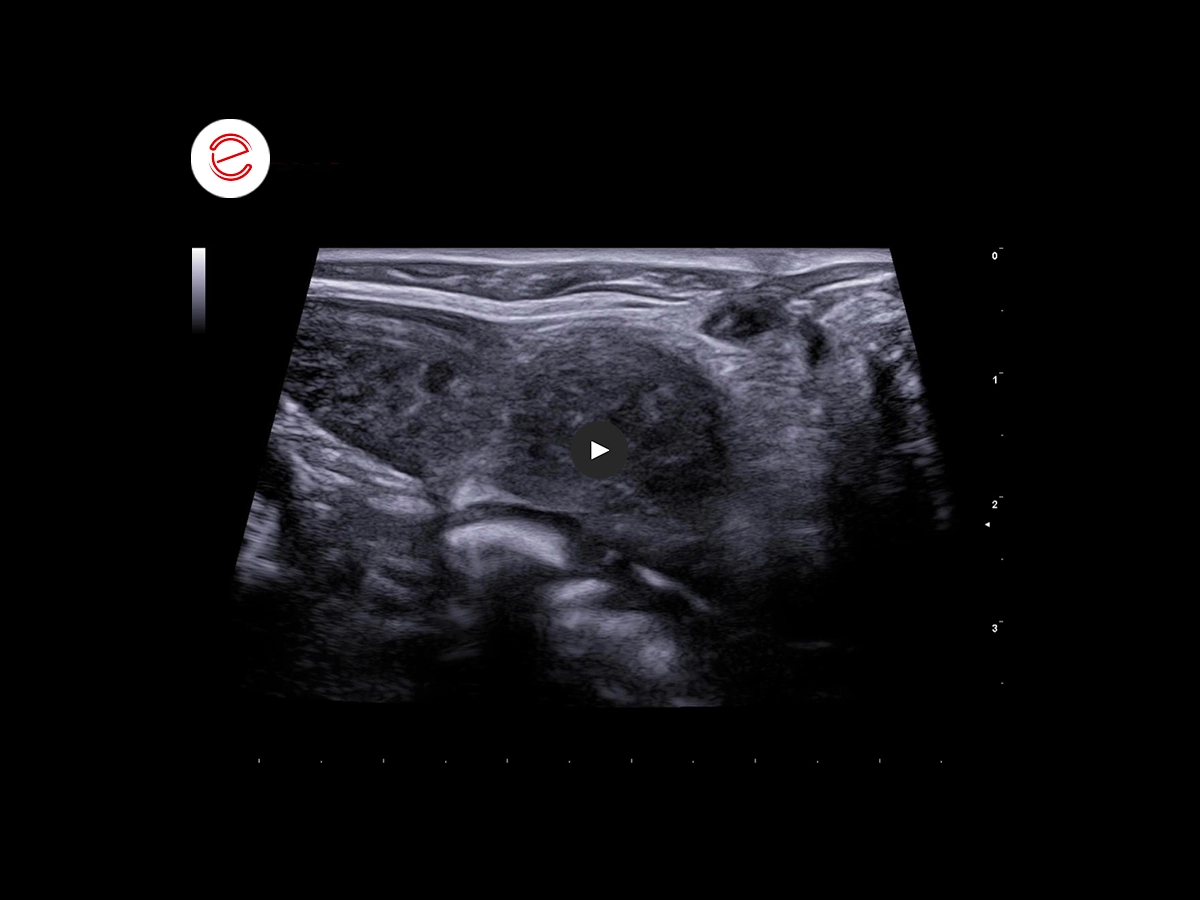
In the liver parenchyma, we note the presence of rounded multifocal lesions, with blurred margins and iso-anechoic heterogeneous echogenicity associated with slight blocking of the organ profile.
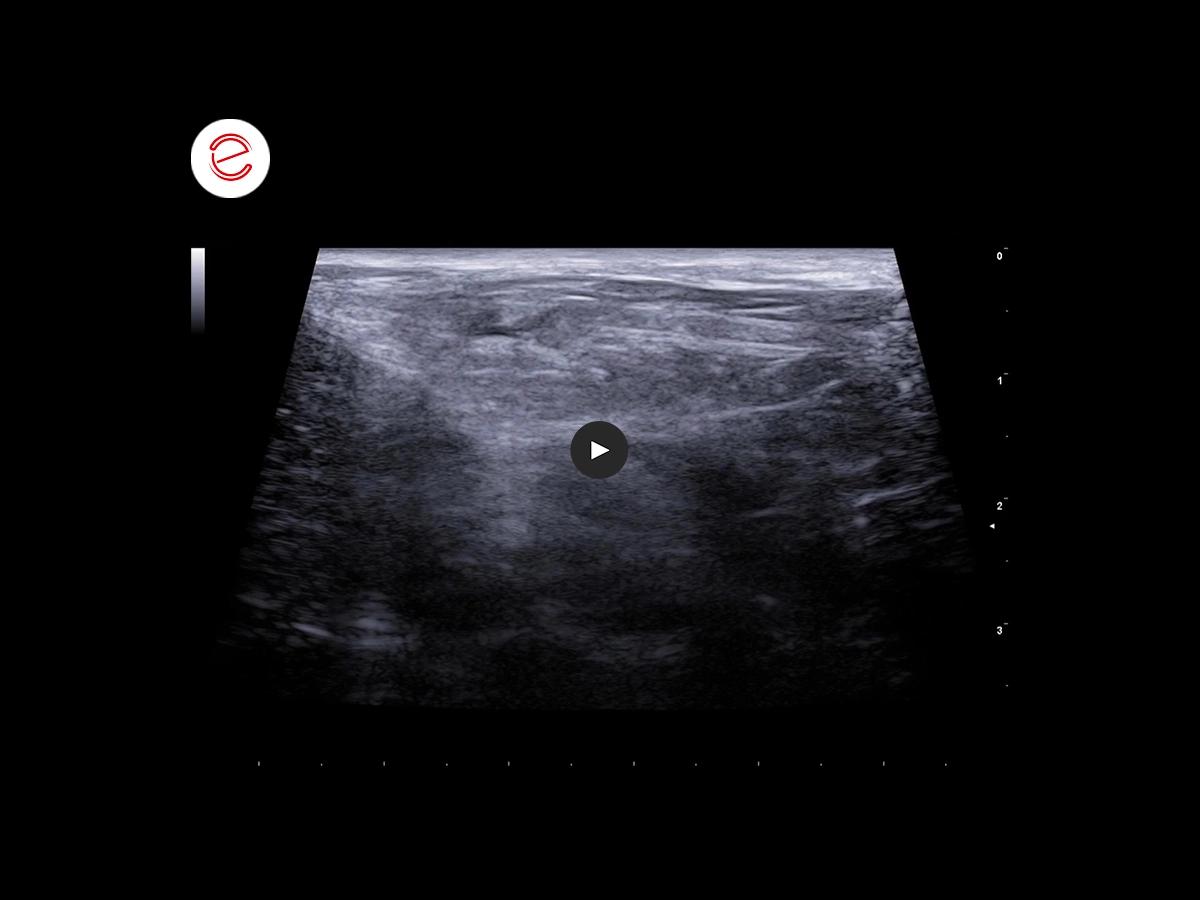
Mild scattering of perihepatic mesenteric adipose tissue.
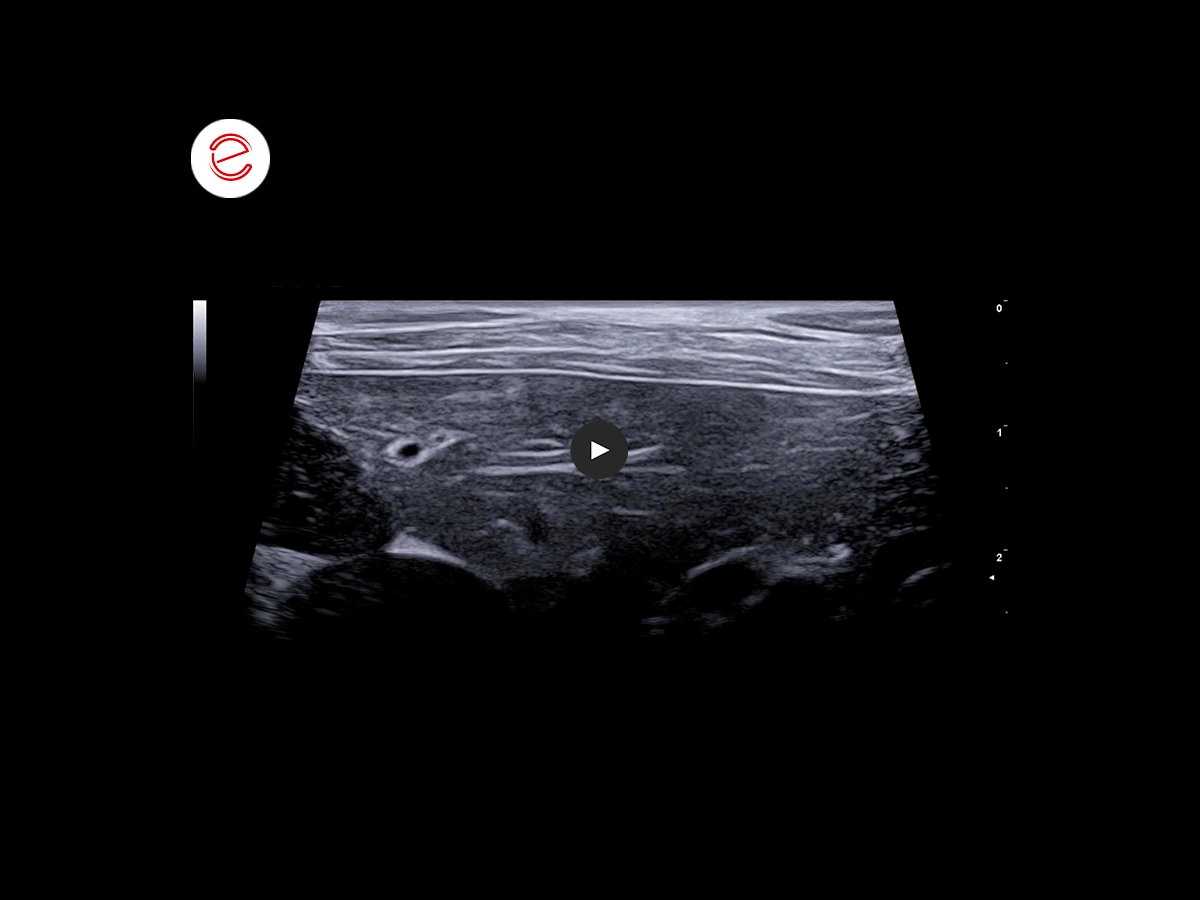
Peritoneal lesions with irregular margins, millimetric, with echostructure and echogenicity similar to the liver lesions described above.
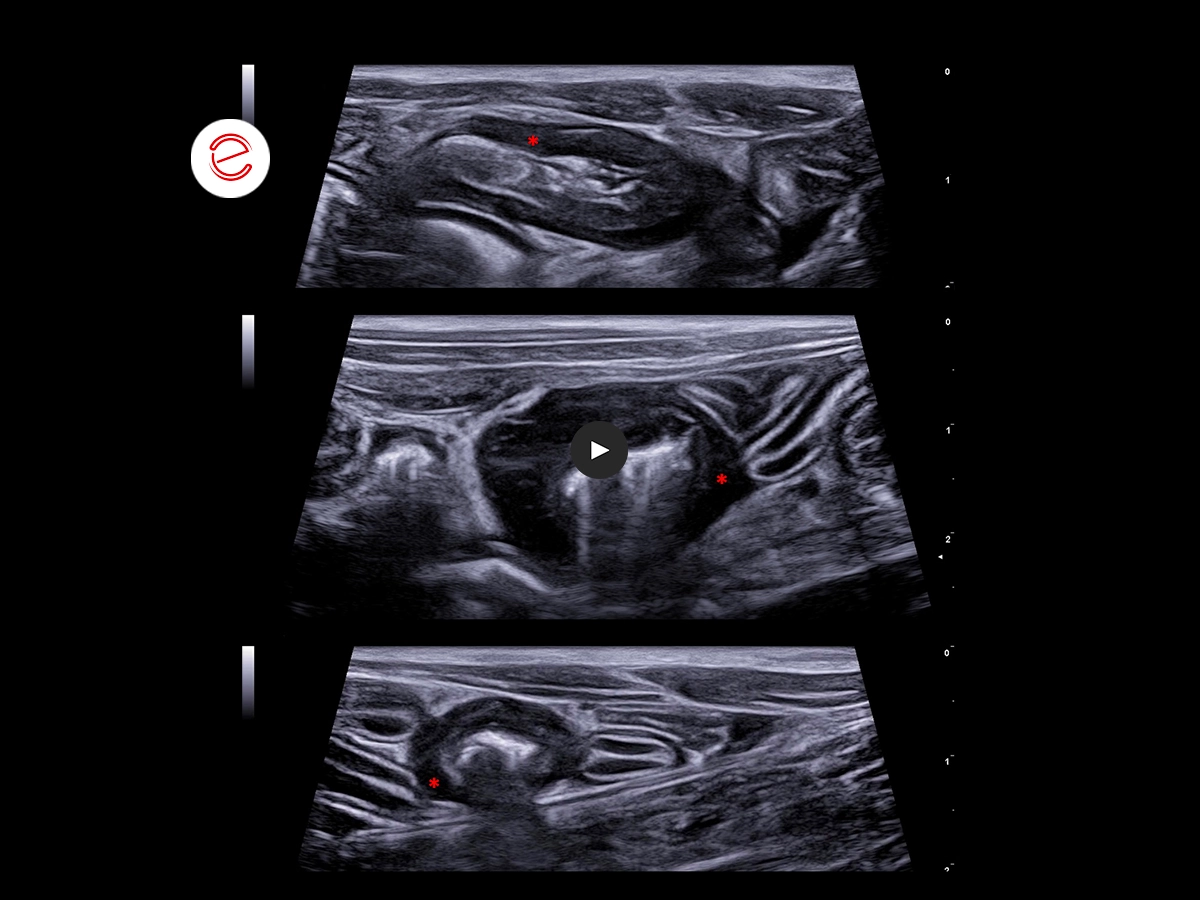
At the gastrointestinal level, multifocal wall thickening with eccentric growth is evident, with partial loss of the stratigraphy, mainly hypoechoic in the absence of mechanical obstruction phenomena.*
We can appreciate:
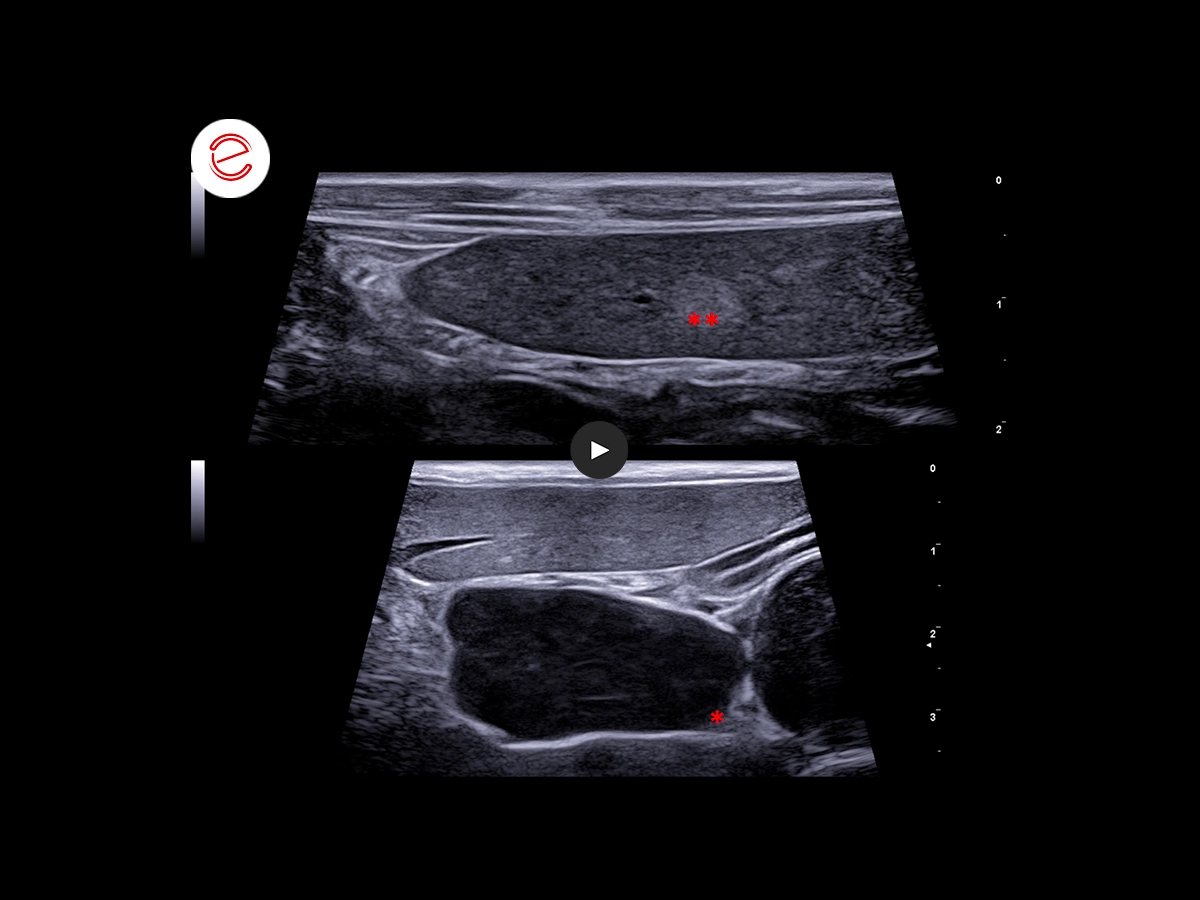
- Generalized abdominal lymphadenopathy, loss of fat hilus, impaired short/long axis ratio, heterogeneous and hypoechoic parenchyma. *
- Heterogeneous and hypoechoic splenic parenchyma with rare round, well-defined and hyperechoic lesions. **
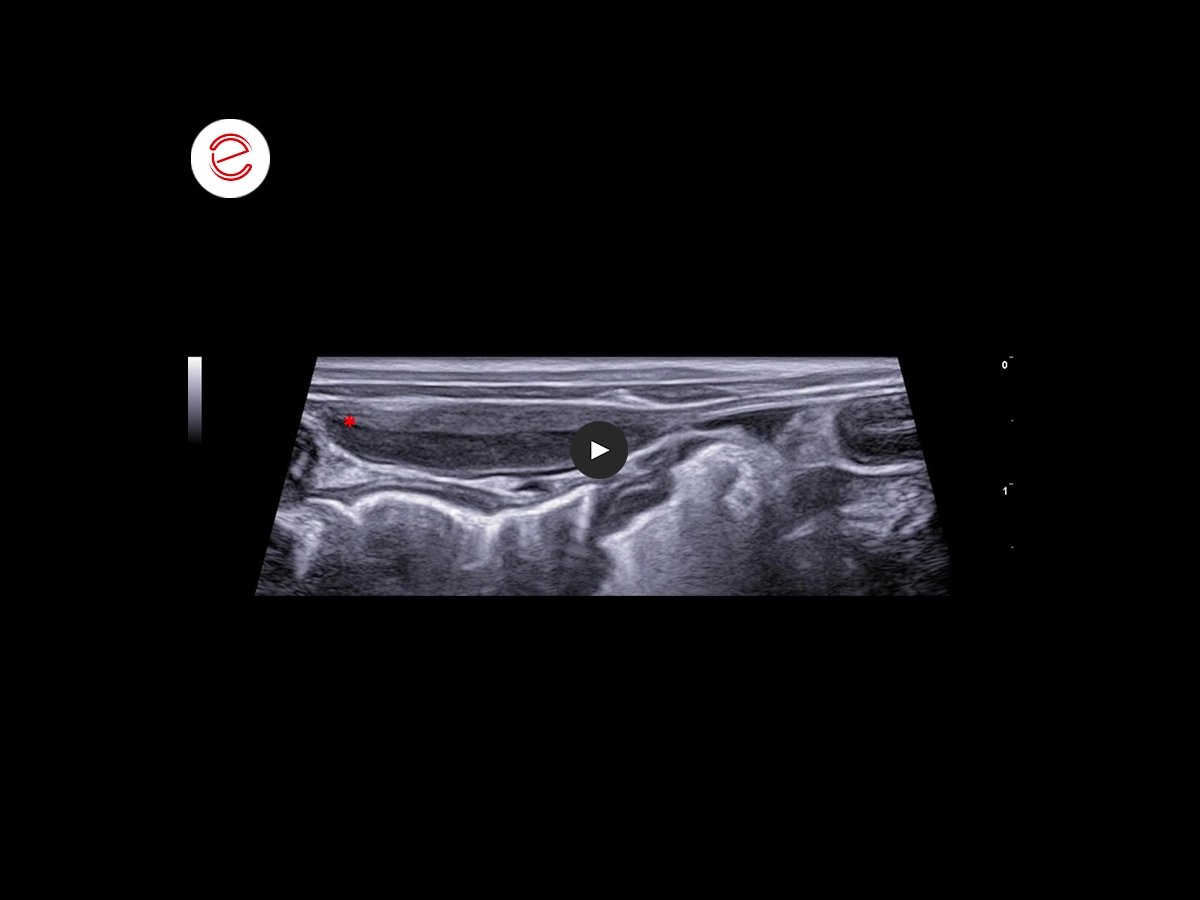
There is mild diffuse peritoneal scattering with little accumulation of anechoic effusion and an infiltrative lesion of the transverse abdominal fascia near the linea alba, iso-hypoechoic to the intestinal muscle.*

We further studied the lymph node vascularization, apparently negative to the Color Doppler signal, using the microV, thanks to which a low flow vascularization was highlighted, with the presence of pericapsular/subcapsular vessels.

FNA of the abdominal visceral lesions is performed with the following outcome: “Cytological picture compatible with malignant round cell neoplasm, in the first hypothesis high-grade lymphoma”.
Images were acquired with MyLab™X8VET ultrasound system.
The speed of some clips could have been modified to improve the visualization of the clinical outcome.
Conclusions and treatment
Patient currently awaiting immunophenotyping and cancer treatment.
Mariaceleste Gendusa DVM, Clinica Veterinaria Gran Sasso, Italy

MyLab is a trademark of Esaote spa.
Technology and features are device/configuration-dependent. Specifications subject to change without notice. Information might refer to products or modalities not yet approved in all countries. Product images are for illustrative purposes only. For further details, please contact your Esaote sales representative.
Other canine clinical cases you may be interested in
Discover the challenges faced, the examinations performed, the solutions adopted, and the treatments recommended.

JUNE 2021
Ventricular septum defect
Claudio Bussadori, DVM, MD, PhD, Dipl. ECVIM (Cardiology)
Clinica Veterinaria Gran Sasso, Milan, Italy

FEBRUARY 2022
Adrenal adenoma
Sergio Fanfoni, DVM, Clinica Veterinaria Santa Cristina
Monte San Savino, Italy, SCIVAC Coordinator

JUNE 2022
Brachial biceps rupture
Laura Martinelli, DVM, MSc
Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, University of Milan, Italy
